Certificate Discovery
1. Introduction
Digital certificates have a limited validity period. In most cases they are rendered useless when they expire. As a consequence, services that rely upon those certificates do not function properly, or they are completely out of service. Several such incidents have happened in the past. Therefore, a reliable mechanism to locate and manage such certificates is necessary to avoid such situations. Additionally, keeping track of all certificates in a system and/or infrastructure is beneficial because it allows to locate misissued certificates. Also, it is possible to more easily enforce policies regarding cryptographic mechanisms or other aspects of certificates.
2. MTG certificate lifecycle manager
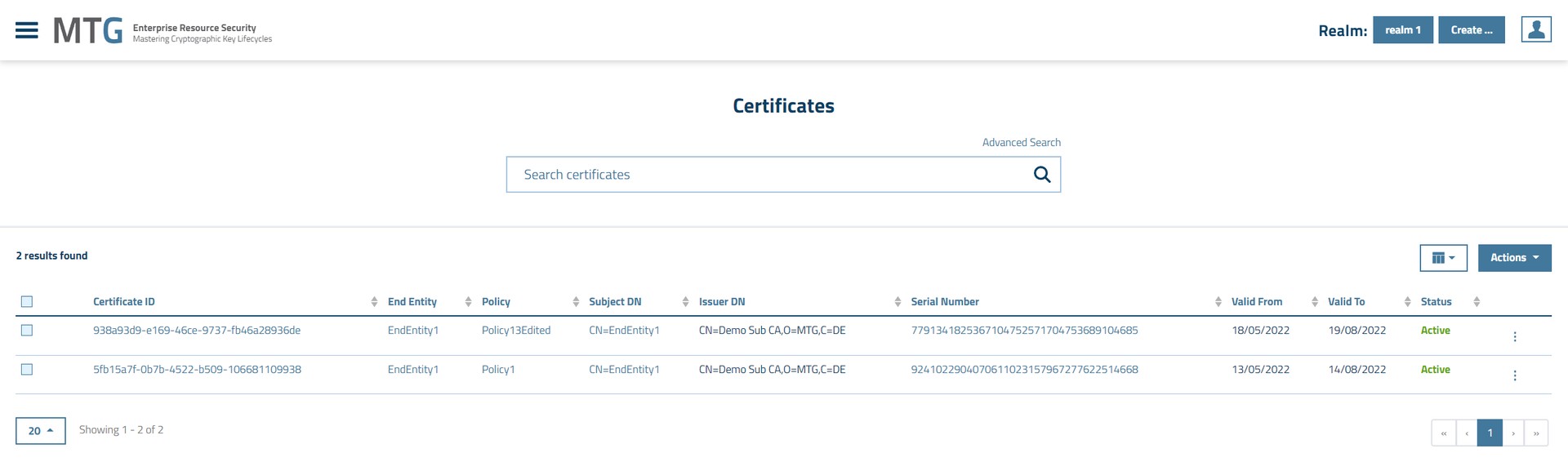
MTG certificate lifecycle manager consists of two components, amongst others. The server and the clients. The server is the standard MTG certificate lifecycle manager application which is the central component of the MTG ERS system. For an illustration of the graphical interface of this component see Figure Figure 1. This component has additionally a REST-API that can be securely accessed by authenticated and authorised clients.
The clients are the so-called ERS cli (Command Line Interface) clients. A cli client is a program that consumes the REST-API of CLM. This cli-client is able to login to CLM and request a certificate. Additionally, it can scan certain ports or port ranges of several other systems located near its network. This can be configured on the command-line interface of the system where an ers client is installed. The installation of an ers client uses typical mechanisms of modern operating systems like rpm or debian packages, or exe files and contains all its dependencies without depending on other resources. See Listing 1, Listing 2, Listing 3, and Listing 4 for examples to configure the servers, IPs, and ports to scan.
ers discover --servers mail.example.comers discover --servers "mail.example.com,web.example.com" --ports "8443,9443"ers discover --servers server1.example.com --ports "8000-9000,9443"ers discover --ips 198.51.100.0/24 --ports "8000-9000"Consecutive calls of ers discover lead to adding additional servers or re-configuring the ports to scan. The standard ports where the cli client scans are shown in Table 1.
| Service | Port |
|---|---|
WEB |
443 |
SMTP |
465 |
LDAP |
636 |
DNS |
853 |
FTP |
989 |
FTP |
990 |
Telnet |
992 |
IMAP |
993 |
POP |
995 |
To scan the configured servers and ports the command shown in Listing 5 needs to be executed. In most cases the command ers scan is placed in a crontab statement with the desired execution time.
ers scanWhen the ers client scans, it tries to establish a TLS connection to the specified server and ports. If it succeeds into establishing a TLS connection it downloads the certificates of the server and pushes them to the CLM component along with some metadata, via a call to the REST-API. The CLM verifies the identity of the client and stores the certificates and metadata into its database. Diagram Figure 2 show a simplified UML sequence diagram of the calls, responsibilities, and involved systems.
Imported certificates and metadata are administered by the application. Examples of metadata is the URL and port where the certificates have been discovered. Typical administration tasks are:
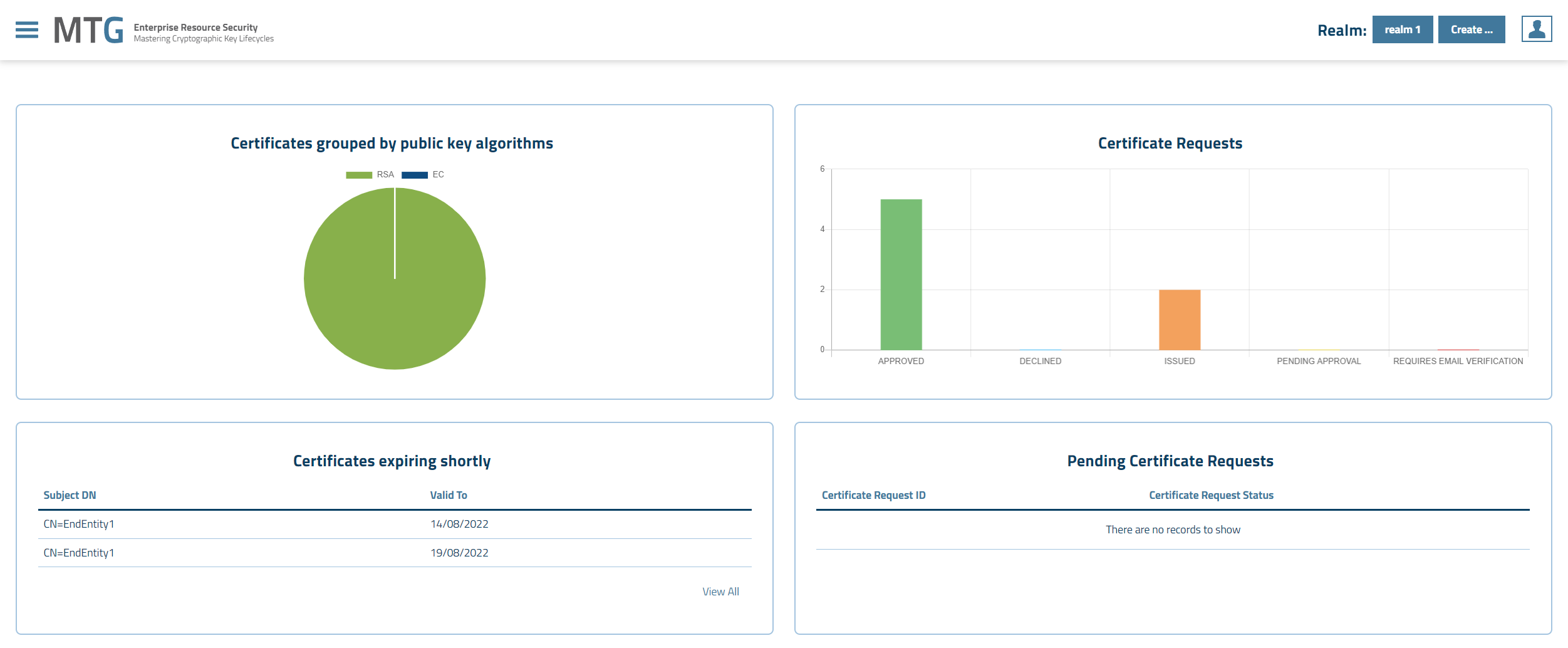
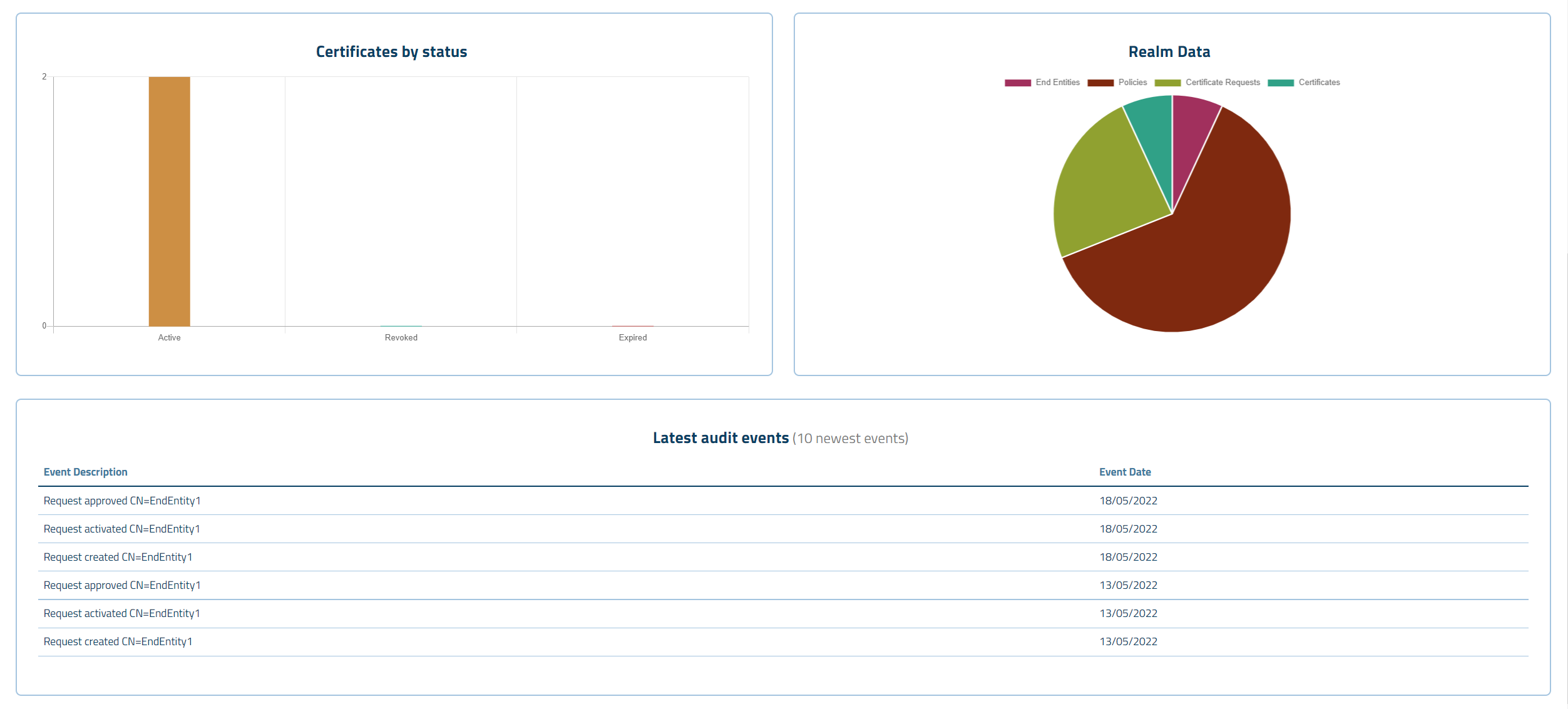
All cli clients themselves can be seen and managed in the GUI of CLM.